When to use past subjunctive in Spanish? Imperfect Subjunctive is one of the easiest tenses in the Spanish language. There is only one simple past tense in the subjunctive mood.
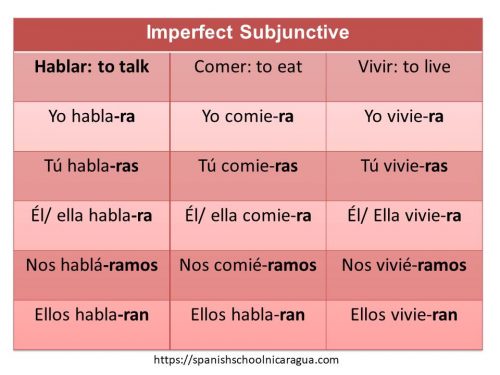
This is formed by adding the following endings to the third person plural of the preterits indicative after dropping the final “on”. For example:
- Ellos comieron: Preterit tense. We drop “on” and we add the endings (a, as, a, amos, an)
- Yo comiera
- Tu comieras
- El comiera
- Nosotros comiéramos
- Ellos comieran
These ending are the same for all three conjugations of regular and irregular verbs: a, as, a, amos, an. Note the accent mark on the Nosotros form. The first person plural bears a written accent over the last vowel before the last “r”
Any stem change or irregularity found in the third person plural of the preterit will be found in all of the past subjunctives of those verbs.
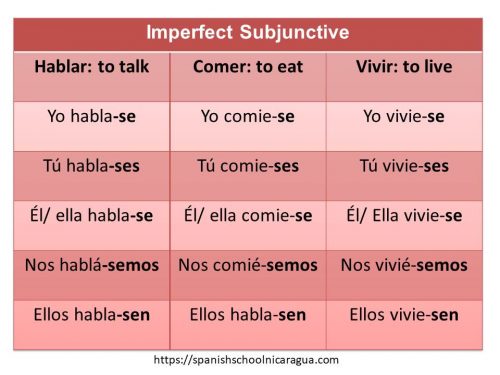
This tense has two forms. The following form is less frequently used in conversation but will be found in literary selections. Video about Imperfect
When we can not use the second form (SE) for Imperfect Subjunctive?
The second form SE is not used in two situations:
- With the verbs: Poder, Querer, Deber. You can not say: Yo pudiese, Yo quisiese o Yo debiese.
- When refers to the preterit tense:
| Infinitive | Preterit | Root | Imperfect Subjunctive |
| Andar | anduvieron | anduvier | anduviera |
| estar | estuvieron | estuvier | estuviera |
| tener | tuvieron | tuvier | tuviera |
| poder | pudieron | pudier | pudiera |
| poner | pusieron | pusier | pusiera |
| saber | supieron | supier | supiera |
| hacer | hicieron | hicier | hiciera |
| venir | vinieron | vinier | viniera |
| decir | dijeron | dijer | dijera |
| ir | fueron | fuer | fuera |
| ser | fueron | fuer | fuera |
Uses
The same noun clauses that require the present subjunctive require the imperfect in the subjunctive when the verb of the main clause is in the imperfect, preterit, or conditional.
- Ella prefería que nosotros saliéramos.
- Prefirió que nosotros saliéramos.
- Ella preferiría que nosotros saliéramos.
This tense is used after impersonal expressions when the main verb is imperfect, preterit, or conditional.
- Era necesario que tu estuvieras presente.
This tense is used in relative clauses modifying an indefinite antecedent when the verb of the main clause is in the imperfect, preterit, or conditional.
- Roberto necesitaba una secretaria que hablara español.
- Juan necesitaría un medico que fuera especialista.
We use the Imperfect Subjunctive to express a desire in a polite way.
Ej: Quisiera una cerveza
Impersonal expressions
The past subjunctive is used after impersonal expressions when the main verb is imperfect, preterit, or conditional.
- Era necesario que tú estuvieras presente.
- Fue necesario que estuvieras presente.
- Seria necesario que estuvieras presente.
What is the difference between the Present Subjunctive and the Imperfect Subjunctive?
In Spanish, the tense, present or past of the main clause verb determines the subjunctive tense in the subordinate clause.
- When the main clause verb is in the present or present perfect, or is a command, a present subjunctive form is generally used in the subordinate clause.
- When the main clause verb is in the preterit or imperfect, a past subjunctive form is used in the subordinate clause.